 |
|
| Mª Carmen García-Rodríguez |
| Toll-like Receptor , Inflammation, Interferon, Metabolism, Cardiovascular diseases, Sphingosine 1-phosphate, NFAT transcription factor |
| Phone: +34-983-184-841 (Office) |
| Phone: +34-983-184-840 (Lab) |
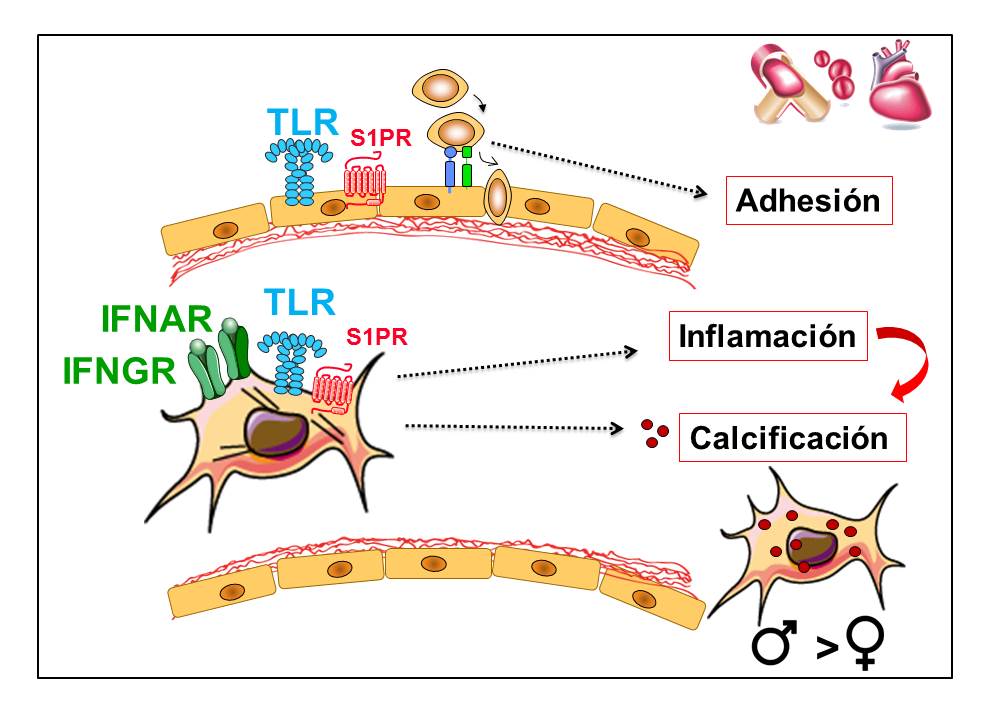
El interés científico del grupo es investigar el papel de receptores de la inmunidad innata en la fisiopatología de enfermedades inflamatorias usando
aproximaciones tanto básicas como traslacionales, usando herramientas de biología molecular e inmunología, así como cultivos primarios de células humanas. Los
receptores tipo Toll o TLR, cuyos descubridores recibieron el Nobel de Fisiología y Medicina en 2011, actúan como centinelas del sistema inmunitario frente a patógenos y a moléculas endógenas procedentes de daño tisular, activando mecanismos de defensa e inflamación. El foco de nuestro estudio es investigar el impacto de estos receptores y de mediadores inflamatorios como
interferones en las fases iniciales de la patogenia de enfermedades cardiovasculares con un componente inflamatorio. Recientemente, el estudio se centra en el papel del metabolismo celular en la fisiopatología de válvulas cardiacas. El objetivo último es diseñar nuevas estrategias terapéuticas para su tratamiento y/o prevención. Las líneas de investigación son:
- Investigar el papel de los TLRs, de inmunomoduladores como los interferones y de moléculas de la matriz extracelular en la patogenia de enfermedades inflamatorias cardiovasculares.
- Elucidar los mecanismos que subyacen a las diferencias según el sexo.
- Estudiar el papel del metabolismo celular en la fisiopatología valvular

 PUBLICACIONES MÁS RELEVANTES
PUBLICACIONES MÁS RELEVANTES
- Sánchez-Bayuela T, Peral-Rodrigo M, Parra-Izquierdo1 I, López J, Gómez C, Montero O, San Román JA, Butcher JT, Sánchez Crespo M, García-Rodríguez C. RE: ATVB/2024/321185: Inflammation via JAK-STAT/HIF-1a drives metabolic changes in pentose phosphate pathway and glycolysis that support aortic valve cell calcification. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2025. DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.322375
- Parra-Izquierdo I, Sánchez-Bayuela T, Castaños-Mollor I, López J, Cristina Gómez C, San Román JA, Sánchez Crespo M, García-Rodríguez C. Clinically used JAK inhibitor blunts dsRNA-induced inflammation/calcification in aortic valve interstitial cells. FEBS J. 2021; 288(22):6528-6542
- Parra-Izquierdo I, Castaños-Mollor I, López J, Gómez C, San Román A, Sánchez Crespo M, García-Rodríguez C. Lipopolysaccharide and Interferon-γ Team Up To Activate HIF-1 via STAT1 in Normoxia and Exhibit Sex Differences in Human Aortic Valve Interstitial Cells. BBA-Molecular Basis of Disease. 2019; 1865:2168–2179.
- Parra-Izquierdo I, Castaños-Mollor I, López J, Gómez C, San Román JA, Sánchez Crespo M, García-Rodríguez C. Calcification induced by type I interferon in human aortic valve interstitial cells is larger in males and blunted by a Janus Kinase Inhibitor. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2018;38:2148-2159.
- Garcia-Rodriguez C, Parra-Izquierdo I, Castaños-Mollor I, Lopez J,San Román JA, Sanchez Crespo M. Toll-like receptors, inflammation, and calcific aortic valve disease. Front. Physiol 2018;9:201.
- Fernández-Pisonero I, López J, Onecha E, Dueñas AI, Maeso P, Sánchez Crespo M, San Román A., García-Rodríguez C. Synergy between sphingosine 1-phosphate and lipopolysaccharide signaling promotes an inflammatory, angiogenic and osteogenic response in human aortic valve interstitial cells. PLoS One. 2014. 9(10):e109081
- Fernández-Pisonero MI, Dueñas AI, Barreiro O, Sánchez Madrid F, Montero O, García-Rodríguez C. Lipolysaccharide and sphingosine 1-phosphate cooperate to induce inflammatory molecules and leukocyte adhesion in endothelial cells. J Immunol. 2012; 189:5402-5410
- López J, Fernández-Pisonero MI, Dueñas AI, Maeso P, San Román A, Sánchez Crespo M, García-Rodríguez C. Exposure of stenotic and non-stenotic aortic valve interstitial cells to bacterial and viral patterns induces sustained TLR-mediated inflammation. Int J Cardiol. 2012;158:18-25
- Dueñas, A., Aceves, M., Fernandez-Pisonero I, Gómez C., Orduña A Sánchez Crespo, M., García-Rodríguez, C. Selective attenuation of Toll-like receptor 2 signalling may explain the atheroprotective effect of sphingosine 1-phosphate. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;79: 537-544
- Dueñas, A. I., Aceves, M., Orduña, A., Díaz, R., Sánchez Crespo M., and García-Rodríguez C. (2006). Francisella tularensis LPS induces the production of cytokines in human monocytes and signals via Toll-like receptor 4 with much lower potency than E. coli LPS. Int. Immunol. 2006;18:785-795.
- Dueñas, A., Orduña, A., Sánchez Crespo, M., and García-Rodríguez, C. (2004). Productive binding of endotoxins to Toll-like receptor 4 correlates with their endotoxic potential and may explain the proinflammatory effect of Brucella spp. LPS. Int. Immunol.2004;16:1467-1475.
- Aceves, M., Dueñas, A., Gomez, C., San Vicente E., Sánchez Crespo, M., and García-Rodríguez, C. (2004). A new pharmacological effect of salicylates: Inhibition of NFAT1 function. J. Immunol. 2004;173: 5721-5729.
- Okamura, H., García-Rodríguez, C., Martinson, H, Qin, J., Virshup, D., and Rao, A. Modulation of NFAT1 activity by multiple kinases in a regulatory complex. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004;10: 4184-4195.
- Okamura, H., Aramburu, J., García-Rodríguez, C.,Viola, J.P.B., Raghavan, A., Tahiliani, M., Zhang, X., Qin, J., Hogan, P., Rao, A. Concerted dephosphorylation of the transcription factor NFAT1 induces a conformational switch that regulates transcriptional activity. Mol. Cell 2000;6: 539-550.
- Macián, F., García-Rodríguez, C., and Rao, A. Gene expression elicited by NFAT in the presence or absence of cooperative recruitment of Fos and Jun. EMBO J. 2000;19: 4783-4795.
INTEGRANTES DEL GRUPO

INTERNACIONALIZACIÓN DEL GRUPO (COLABORADORES)
- Dra. Maria Teresa Cruz, Universidad de Coimbra, Portugal
- Dra. Taina Pihlajaniemi, Oulu University, Finlandia.
- Dr. Adrian H Chester, Imperial College, National Heart & Lung Institute, Gran Bretaña
- Dr Jonathan T Butcher, Meinig School of Biomedical Engineering, Cornell University, USA
TESIS DOCTORALES DIRIGIDAS Y SITUACIÓN ACTUAL DE EGRESADOS
- Lourdes del Río Solá. 2007. Efecto del ácido acetil salicílico en la úlcera venosa de la extremidad inferior y en la expresión génica de quemoquinas proinflamatorias en venas con insuficiencia venosa crónica. . (Jefe de Servicio y Adjunto de Angiología y Cirugía Vascular, HCUV, y Profesor Asociado de la UVA).
- Mónica Aceves Tejero. 2007. Estudio de la regulación del factor de transcripción NFAT1 y de su modulación farmacológica por salicilatos y derivados trifluorometilados. (Evaluador y análisis de proyectos tecnológicos de I+D, CDTI).
- Mª Isabel Fernández Pisonero. 2013. Receptores tipo Toll y de esfingosina 1-fosfato y su implicación en la fisiopatología cardiovascular (Investigadora postdoctoral, Centro de Investigación del Cáncer, Salamanca).
- Iván Parra Izquierdo. 2019. Effects of interferons and their interaction with other ligands in human aortic valve cell. (Senior scientist, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ridgefield, CT, USA).
- Irene Castaños-Mollor Morcillo. 2020. El colágeno tipo XIII en la patogenia de la estenosis aórtica calcificada. R&D Project manager, CNIO
- Tania Sánchez-Bayuela Recio. 2023 Metabolic rewiring is required for inflammation, calcification and osteogenic differentiation in human aortic valve interstitial cells exposed to an inflammatory milieu and mimics the metabolic phenotype of calcified aortic valves. Investigadora Postdoctoral en Centre de Recherche des Cordeliers, Paris, France
- Mirian Peral Rodrigo. Inmunidad, metabolismo y estrés de retículo en la patogenia de la estenosis aórtica calcificada. En progreso.
A DESTACAR
El grupo pertenece al Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Cardiovasculares (CIBERCV) del Instituto de Salud Carlos III, lo que permite realizar estudios de naturaleza traslacional combinando el uso de cultivos primarios de muestras de pacientes con técnicas de biología molecular.
ENTIDADES FINANCIADORAS



 PUBLICACIONES MÁS RELEVANTES
PUBLICACIONES MÁS RELEVANTES


